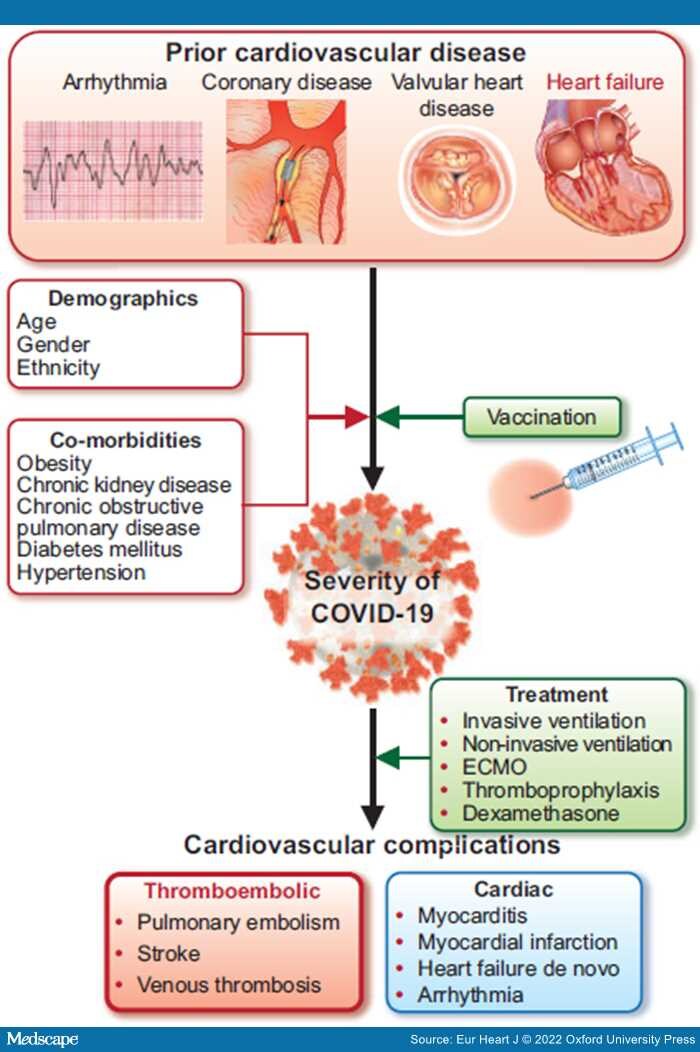
Graphical Abstract: The bidirectional relationship between cardiovascular disease and COVID-19 infection. ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
The recent outbreak of a novel coronavirus illness (coronavirus disease 2019; COVID-19) has emerged as a public health crisis of global proportions. The cardiology community has been captivated by COVID-19, perhaps more than any other systemic disease in history, due to its apparent links with cardiovascular disease (CVD). Researchers rapidly pivoted attention to concentrate on the disease, with initial case series and single-centre studies suggesting poor outcomes in patients with prior cardiac conditions and, soon after, reports of a high prevalence of cardiovascular complications. However, now, more than a year since the pandemic's onset, larger studies have emerged that are beginning to refine our understanding of the complex interplay between COVID-19 and CVD.
Previous COVID-19 studies have predominantly evaluated the association between pre-existing chronic cardiac disease and COVID-19-related mortality, where all cardiac conditions are combined and analysed together.[1–3] In this issue of the European Heart Journalthe CAPACITY-COVID and LEOSS (Lean European Open Survey on SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients) study groups report on their collaborative retrospective study using coordinated large-scale data collection to evaluate heterogeneity in associations between various heart disease subtypes and in-hospital mortality.