Abstract and Introduction
Introduction
Clinical presentation and pertinent laboratory analysis often determine the appropriate imaging differential diagnostic considerations in evaluating anyone with ovaries presenting with pelvic symptoms. In patients with a positive pregnancy test, sonography is the modality of choice to evaluate the pregnancy and any complications. Sonography is also the modality of choice for evaluating patients who present with pelvic pain or a mass but are not pregnant. Pelvic sonography is the preferred imaging modality when an obstetrical or gynecologic etiology is suspected under American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria.[1]
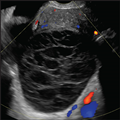
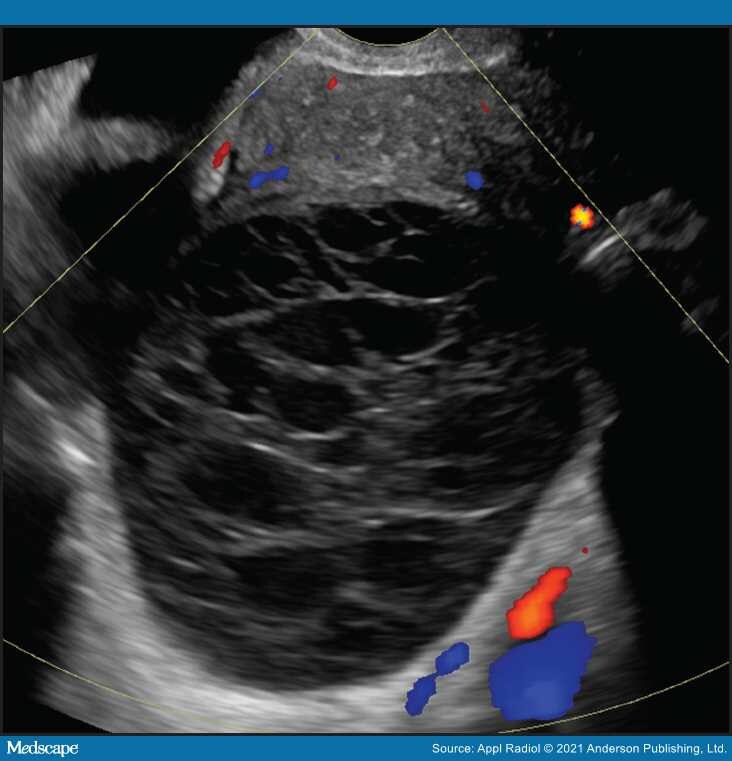
Sonography is useful in evaluating for the presence of an adnexal mass as well as for mass characterization.[2] For example, the sonographic appearance of a retracting clot and/or a reticular pattern without Doppler flow/vascularity is diagnostic of a hemorrhagic cyst (Figure 1).[3] Most adnexal cysts are benign and are easily characterized by ultrasound. However, evaluation of indeterminate adnexal masses by an ultrasound expert is highly valuable.[3] Published data supports the use of pattern recognition by an experienced ultrasound examiner as a highly accurate method of discriminating between benign and malignant adnexal masses without the need for MRI.[3] In particularly challenging cases, contrast-enhanced MRI may be helpful in differentiating between benign and malignant ovarian masses.
Figure 1.
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst. Typical reticular pattern of fine, thin intersecting lines representing fibrin strands with no central flow is one pattern of a hemorrhagic cyst (O-RADS 2).
This two-part review describes a stepwise approach to evaluating and characterizing adnexal masses in non-pregnant patients. Here in part 1, we will review the utilization of ultrasound in this endeavor. In part 2, we will review the use of MRI.
Appl Radiol. 2021;50(3):24-31. © 2021 Anderson Publishing, Ltd.